What is musculoskeletal pain?
Musculoskeletal pain is chronic or intense pain that affects joints, bones, and muscles. It is a common problem that effects almost one- third of the UK population ranging from minor injuries to long term conditions such as arthritis or back pain. Musculoskeletal disorders are characterised by a consistent pain that negatively effects movement and quality of life.
Pain effecting the body for longer than 3 months is referred to as chronic musculoskeletal pain, which not only becomes a physical problem but has a significant impact on wellbeing and mental health. This can vary between patients but in some individuals, it can lead to a complete loss of independence and almost half of those with chronic pain also suffer with depression.
What causes musculoskeletal pain?
There are over 200 different causes of chronic musculoskeletal pain, that each affects different areas of the body. The main causes of pain are categorised into three main areas for concern; joint, muscle and bone. This involves a variety of conditions where an individual may suffer from one or multiple causes of pain. Musculoskeletal pain can be caused by trauma to an area such as falls, fractures or dislocations. Other causes of pain can include postural strain or overuse. joint, bone or muscle pain
Musculoskeletal conditions
The musculoskeletal system includes bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons and soft tissues. It provides movement to the body as well as support and stability. Therefore, there are several factors that can contribute to musculoskeletal pain.
Musculoskeletal conditions affect the following:
Joints
- Mechanical back pain
- Inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis etc.)
- Osteoarthritis
- Gout or pseudogout
- Joint hypermobility
Bones
- Compression fractures of the spine
- Acromegaly
- Paget’s disease
Muscles (and tendons)
- Myositis
- Tendinitis
Musculoskeletal pain symptoms
The symptoms associated with chronic musculoskeletal pain will depend on the underlying cause of the pain. The pain may be mild or severe and vary in terms of acute or chronic musculoskeletal pain. The most common pain locations are back, hips and knees. Since many types of musculoskeletal pain are associated with a reduced range of movement this can result in limited function and restriction of activities.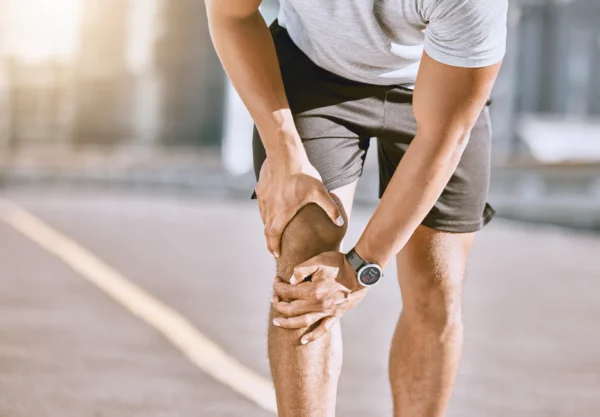
Musculoskeletal pain treatment
A holistic approach is often needed to treat chronic musculoskeletal pain. This can include physiotherapy, psychological therapies and modifications to your home and work environment. Medical therapy is dependent on the underlying cause of pain, which is an important component of treatment. For muscle and connective tissue pain, simple painkillers are often used as a first-line treatment. Then stronger painkillers (e.g., codeine, tramadol and morphine) can be used in conjunction for severe pain. Specialist medications for conditions such as inflammatory arthritis are prescribed to help regulate the immune system. In addition to medication, it is also important to try and continue exercising as tolerated. However, some conditions such as osteoarthritis of the hip or knees may benefit from an operation when severe.
Musculoskeletal Pain Diagnosis
Chronic musculoskeletal pain is diagnosed by a specialist doctor. This will involve a thorough examination to identify the type of pain, severity and symptoms. Some patients may benefit from X-Rays to discover any problems with bones, as well as an ultrasound or MRI scan of the affected areas. A clinician may make recommendations for other investigations, such as blood tests to look for signs of inflammation or joint aspiration, depending on the underlying cause of the pain.
Medical Cannabis for Musculoskeletal Pain

Managing musculoskeletal pain effectively often requires a comprehensive approach, combining physical therapies, medications and lifestyle adjustments. Chronic pain is the most common condition for which medical cannabis is prescribed at Curaleaf Clinic and there is growing real world evidence on patients prescribed medical cannabis for chronic pain through the UK Medical Cannabis Registry.
To check your eligibility for a consultation with a pain specialist at Curaleaf Clinic fill out our ten-minute online form and submit your medical records.

